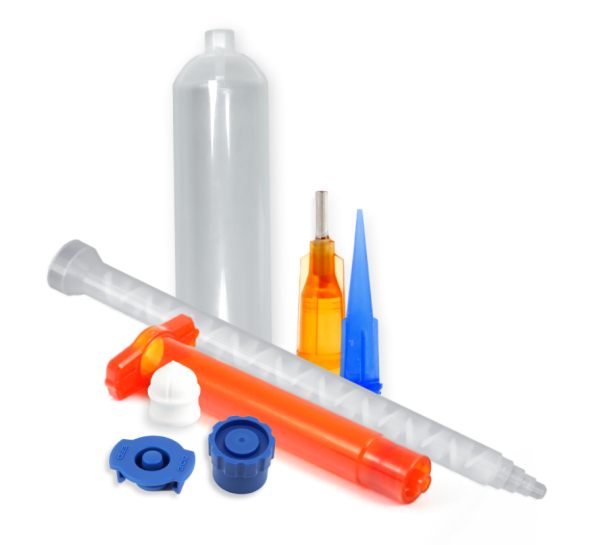
Ideal static mixer for your application
A static mixer (also called a motionless mixer or mixing nozzle) is a simple device with no moving parts, and consists of a series of internal elements (baffles) within a plastic housing (tube).
The static mixer is the central, if not the most important, part of the two-component dispensing system.

Theory of Static Mixing
Elements within the mixer stay “static” i.e. they do not move.
The A & B materials are pushed/pumped/injected into the static mixer in the ratio required. As the two materials move through the series of alternately-angled elements, they are forced to come together and apart, over and over again.
This flow creates layer upon layer of A & B materials. Eventually, the material has been layered so many times, that A & B become a homogeneous stream when they exit the mixer outlet.

Static Mixers optimized for specific fluid types
| Material Typical # of Elements | |
| Acrylic | 8 – 20 |
| Epoxy | 15 – 24 |
| Polysulfide | 24 – 32 |
| PU Foam | 10 – 24 |
| Silicone | 20 – 30 |
| Urethane | 24 – 36 |
| Viscosity range Mixing element diameter range | |
| Thin < 5 000 cps – thinner than syrup | 0.093” – 0.25” (2.36 – 6.35mm) |
| Middle 5 000 – 50 000 cps – thicker than honey, less than ketchup | 0.212” – 0.314” (5.4 – 8mm) |
| Thick > 50 000 cps – thicker than ketchup | > 0.366” (9.3mm) |
When mixing liquids of two different viscosities, we always choose the mixer based on the component with the higher viscosity
Each type of finish provides specific advantages for specific applications